Level of the Free Gingival Margin
1. The level of
free gingival margin in relation to cementoenamel junction (FAC) should be recorded on a dental Chart. This level may simply be painted on the face and lingual surfaces of the dental Chart.
2. Several possible relationships exist between the free gingival and FAC:
a. Free gingival margin may be slightly coronal (above) FAC. This is a natural level of the gingival margin and represents the expected position of the gingival margin in the absence of disease or injury.
B. Free gingival margin can be significantly coronal to FAC. Gingival margin can be coronal to FAC because (1) swelling (edema),
(2) overgrowth (as seen in patients taking certain medications), and/or
(3) increase of fibrous connective tissue (as in the old tissue inflammation).
c. Free gingival margin is apical to FAC. This relationship, as you know recession gingival margin, the impact on the parts of the root surface. Gum recession margin is defined as the place of the gingival margin apical to cementoenamel isolation as a result of irradiation of the surface of the root.
[1]
3. Field 19-1 the methods to determine the free level of the gingival margin.
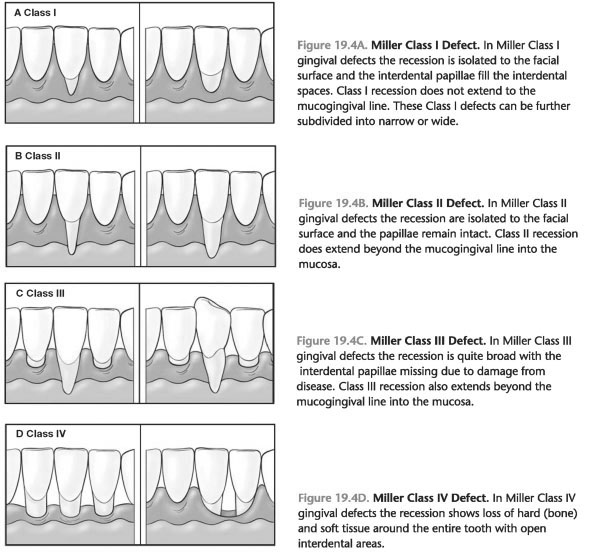
4. When the gingival margin is apical to the FAC (i.e., gingival recession is present), the seriousness of the recession gingival margin, usually classified Miller classification system of gingival recession. This system is presented in Fig. 19-4A-d
When tissue swelling or recession is present, periodontal probe is used to measure the distance of the gingival margin is apical or coronal to FAC. Keep in mind that a natural or expected level of gingival margin in the absence of disease or injury slightly coronal to FAC.
1. To gingival recession. If the gingival recession is present, the distance between the FAC and the gingival margin is measured using a calibrated periodontal probe. This distance is recorded as the level of the gingival margin.
2. For gingival enlargement. If gingival enlargement is present, the distance between the CEJ and the gingival margin is also measured using a calibrated periodontal probe. This distance is estimated using the following technique:
a. The position of the tip of the probe is at an angle of 45 degrees to the surface of the tooth.
B. Slowly move the probe under the gingival margin before crossing between the enamel and cement detected.
c. Measure the distance between the gingival margin and FAC. This distance is recorded as the level of the gingival margin.
 ..
..
 ..
..