Oral epithelium
Oral epithelium veils the outer surface of free gum and attached gingiva; it stretches from the crest of the
gingival margin to mucogingival junction. OE is only part of periodontal that are visible to the naked eye (Fig. 2-5).
And cell structure of epithelium cavity (OE)
1. Th may be dead or parakeratinized (partially dead). Keratin is the tough, fibrous structural protein that occurs in the outer layer of skin and original.
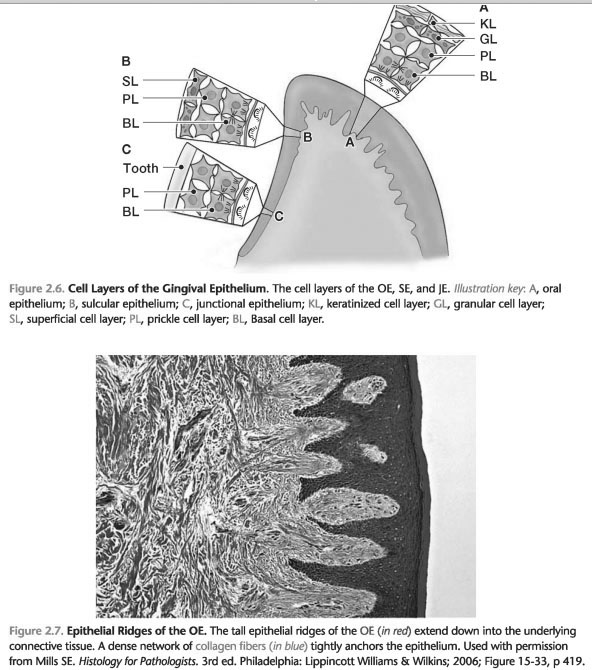
2. OE is a multi-layer flat epithelium, which can be divided into the following layers of cells (Fig. 2-6):
a. Basal cell layer: cube-shaped cells
B. The Bush layer of cells: spinelike cells with large intercellular spaces. Cells, as basal and thorn layers of cells to attach to each other with desmosomes.
c. Granular layer of cells: flat cells and increase intracellular keratin.
d. The Horny layer of cells: flat cells with a large intracellular keratin.
B. the interface with the connective tissue of the gums.
In health, the original connection with connective tissue in wavy interface with epithelial ranges (Fig. 2-5 and 2-7).
2. Sulcular Epithelium. Sulcular epithelium (SE) of the epithelial lining of the gingival sulcus. It stretches from the crest of the gingival margin to coronal edge JE (Fig. 2-5).
A. cellular structure Sulcular epithelium (SE)
1. SE is a thin, nonkeratinized epithelium [2].
2. The DPP has three cell layers (Fig. 2-6):
a. Basal cell layer
B. The Bush layer of cells
c. The surface layer of cells: flat cells, without keratin
3. SE skips allows the fluid to drain from the connective tissue of the gums in the furrow. This fluid is called gingival crevicular fluid. The inflow of gingival crevicular fluid slightly health and increase of the disease.
B. the interface with the connective tissue of the gums. In health, sulcular epithelium joins connective tissue on a smooth interface, which is not epithelial ranges (not wavy junction) (Fig. 2-5).
3. Paroxizmalnaya Form Epithelium. Paroxizmalnaya form epithelium (JE) is a specialized epithelium, which forms the basis of the furrow and associations of the gums to the tooth surface (Fig. 2-5).
The gums around the neck of the tooth and is attached to the tooth using paroxizmalnaya form epithelium. Base furrow consists of coronal-most of the cells paroxizmalnaya form epithelium. In health, JE gives a tooth at a level that is slightly coronal to cementoenamel junction.
A. cellular structure paroxizmalnaya form epithelium (JE)
1. Keratinization JE
a. In paroxizmalna form of an epithelium of a thin, nonkeratinized epithelium.
B. Nonkeratinized epithelial cells as sulcular and paroxizmalnaya form areas gingival epithelium to make them less effective protective coating. Thus, sulcular paroxizmalnaya form and districts to provide a single point of entry for bacteria and bacterial products to invade the connective tissue of the gums.
2. In paroxizmalna form epithelium has only two layers of cells (Fig. 2-6):
a. Basal cell layer
B. The Bush layer of cells
3. The length and width JE
a. In paroxizmalna form epithelium ranges from 0,71 to 1.35 mm [3].
B. The joint venture is approximately 15 to 30 cells with a thickness in the estuarine zone-the zone, which gives higher crown of the tooth.
c. JV narrows down to 4 - 5-cell thickness in the apical zone.
B. JE interface with the connective tissue of the gums. In health, paroxizmalnaya form epithelium has a smooth fabric interface with connective tissue (not wavy junctions) (Fig. 2-5).
 ..
..
 ..
..